In this article
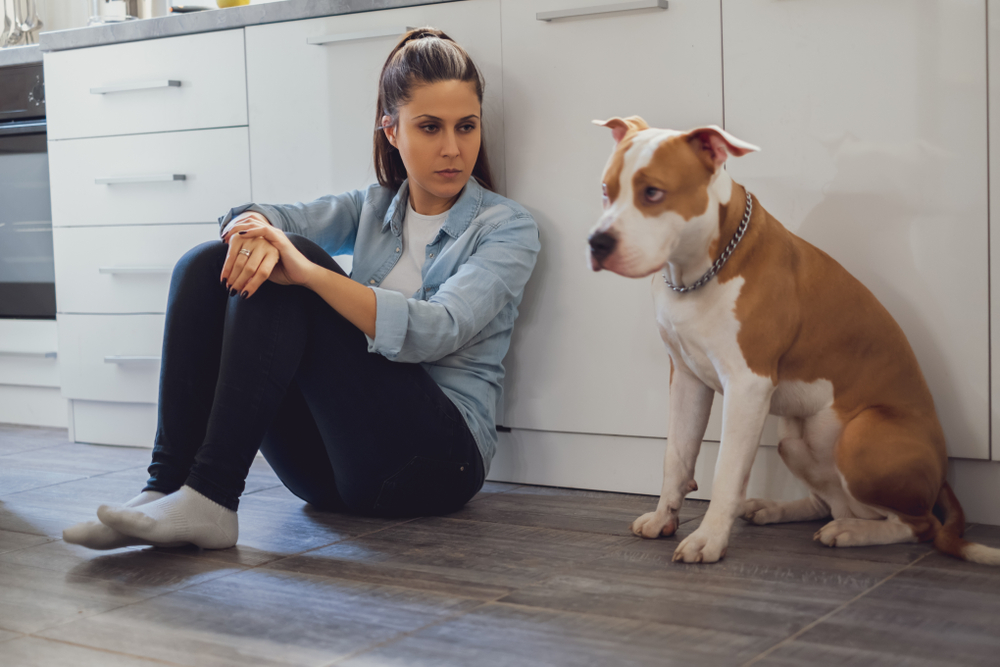
Dogs have been man’s best friend for thousands of years, so it’s become second nature to attribute human-like behavior to the things they do. For instance, you may have seen your dog seemingly holding a grudge, which means exhibiting spiteful, resentful, or retaliatory behavior. Maybe you got upset and raised your voice at them or simply left the house for too long, and now your dog is acting out. Can dogs actually hold grudges, though?
No, dogs can’t hold grudges in the same way that humans can. While there is little research in the area, we do know that dogs can experience negative and positive emotions, and they have cognitive capacity and remembrance. That said, even though a dog can remember a negative experience, it is unlikely that they will spend their time replaying that experience in their mind and thinking about revenge. The way that dogs experience emotions and handle negative events is far more instinctual and reaction-based. Dogs don’t know what “fair” is in human terms, just what is, and they learn from it by building associations with good things and bad things—positive and negative associations, respectively.
Dogs rely on associations to navigate the world. They might choose to ignore, avoid, bark, or snap at a person who’s mean to them but happily welcome their beloved owners home with a tail wag and face licks. For more about how dogs experience emotion, how exactly that’s different from a grudge, and how to handle grudge-like behavior, keep reading.

Dog Emotions vs. Human Emotions: What’s the Difference?
While we can’t reach into their heads or ask them what they feel, we know that dogs don’t feel emotions in exactly the same way we do. At the risk of simplifying the matter, dog emotions are less complex and lack the social context that our emotions do. What does that mean, exactly?
- Social context: Human emotions are influenced and contextualized by society, culture, and our social relationships. Meanwhile, dogs form close familial bonds but otherwise aren’t affected by those human factors.
- Emotional range: There’s some debate on exactly which and to what degree, but most agree that dogs can’t experience certain emotions like pride, resentment, or shame. However, they can feel emotions like fear, joy, anger, and sadness1.
- Body language: Dogs can’t talk to express themselves, so they rely on body language to convey their emotional state to you.
- Emotional Metacognition: Humans can reflect inward on their emotions and effect change on them. While studies suggest that dogs have a certain degree of metacognition2, it is likely used in practical scenarios, not to reflect on their emotional state.

Dog Emotions Are Based on Association & Avoidance
Dog emotions are largely founded on positive and negative mental associations formed by stimuli and outcomes. In a way, your dog instinctively understands cause and effect, but mainly from past experiences and with limited ability to extrapolate or recontextualize this to future events.
The famous Pavlov experiment is a classic example of positive association. In the experiment, Pavlov rang a bell before mealtime, and the dogs began to associate the bell with the food that came immediately after. They would salivate at just hearing the bell, just like how many dogs today go wild when they hear a bag of kibble or another rattling container that sounds similar. Positive reinforcement training techniques take advantage of this to sort of rewire the way your dog feels in response to certain desirable behaviors.
On the flip side, you have avoidance, a dog’s natural instinct for avoiding situations, people, places, or animals based on negative past experiences. Dogs avoid anything they have a negative association with, which ranges from loud noises, mean guests, past abuse, aggressive animals, and more. If possible, dogs will avoid these by running away and/or hiding. If they’re unable to do so, this can cause them significant stress, which might even lead to aggression because they can’t understand and work through the problem like humans.
Sometimes, stressed-out dogs, as dog owners know, often act out via destructive behaviors like chewing, digging, or scratching. These are a dog’s way of self-soothing when they’re stressed, like how some people bite their nails or pick at their face.
If your dog seems like they’re holding a grudge, don’t take it personally—they’re reacting to something that happened (stimulus) and not actively nursing a grudge toward you.
To help your dog work through negative associations, you need to replace them with positive associations in a process called counterconditioning. For example, teach your dog that storms aren’t scary by acting matter-of-fact and rewarding calm behavior in place of previously fearful behavior.
Dogs are highly incentivized to seek rewards and please you, so counterconditioning is an excellent way to ameliorate “grudge-like” behavior.
- Locate the stimulus/trigger: Does your dog whine at the sound of thunder, or maybe they always bark at the same dog that was mean to them a long time ago? You need to first identify what is triggering your dog.
- Introduce the stimulus: Start slow. For example, with storm anxiety, play the sound of thunder at a very low volume.
- Reward calm behavior: Before your dog reacts to the stimulus in a negative way, reward them while they’re still calm.
- Ramp it up: Slowly increase exposure to the stimulus in a controlled, measured way. Using the storm example, you’d increase the volume of the storm sounds.
- Ignore avoidant behavior: Whining, barking, hiding, or running away should be carefully ignored without accidentally building a negative association—do so by radiating a statue-like calm your dog can see.
- Use high-value treats: Use a delicious piece of boiled chicken or something your dog goes absolutely bananas over.
- Don’t overdo it: Take things at your dog’s pace and keep sessions short, as exposure to stressful stimuli for too long can have the opposite effect from what you want.


Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are Some Dogs More Likely to Seem Like They Hold Grudges?
Yes, some dogs are more likely to seem like they’re holding a grudge, but it’s not them being vengeful—they might just be more sensitive to negative stimuli or more prone to anxiety than other dogs. For example, some strong-willed dogs won’t bat an eye if you raise your voice a little, but other dogs might be very fearful and resort to self-soothing behaviors.
Can Dogs Hold Grudges Against Other Animals?
Dogs can’t stay mad in the long term at other animals in the way we can stay mad at other people. Any avoidant or aggressive behavior in response to dogs, cats, or other animals is due to things like a perceived threat, if your dog is guarding resources like food, or if they’ve had a negative past experience with an animal that looks similar.

Do Dogs Understand When Humans Are Mad at Them?
Dogs can understand human emotions to a shocking degree, and yes, they understand when you’re mad at them but not why3. Your dog simply knows that your body is tense, your face is scrunched up, and you’re exhibiting other body language cues you may not even know about yourself. In response, your dog might cower, hide, run away, or assume a submissive posture, like showing their belly.

Wrapping Up
Dogs can’t hold grudges the way that humans do, but how they avoid negative associations can seem like a grudge to humans who don’t know any better. If your dog acts like they’re holding a grudge, you should first figure out what’s triggering their avoidant behavior. Once you know what the cause is, you can carefully utilize counterconditioning training methods to replace their fear with a positive response.
Featured Image Credit: Sjale, Shutterstock