In this article
View 4 More +Many pet parents ponder this question as they weigh the decision to spay their furry companion. While a large amount of data states that spaying does indeed increase a dog’s lifespan, a few studies suggest otherwise.
Here, we discuss what scientists know so far about the potential impact of spaying on a dog’s longevity.

What Every Dog Parent Should Know About Spaying
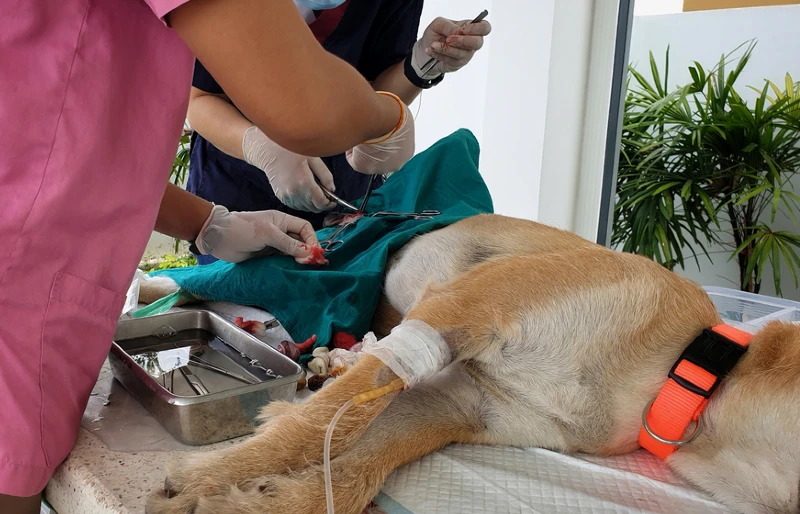
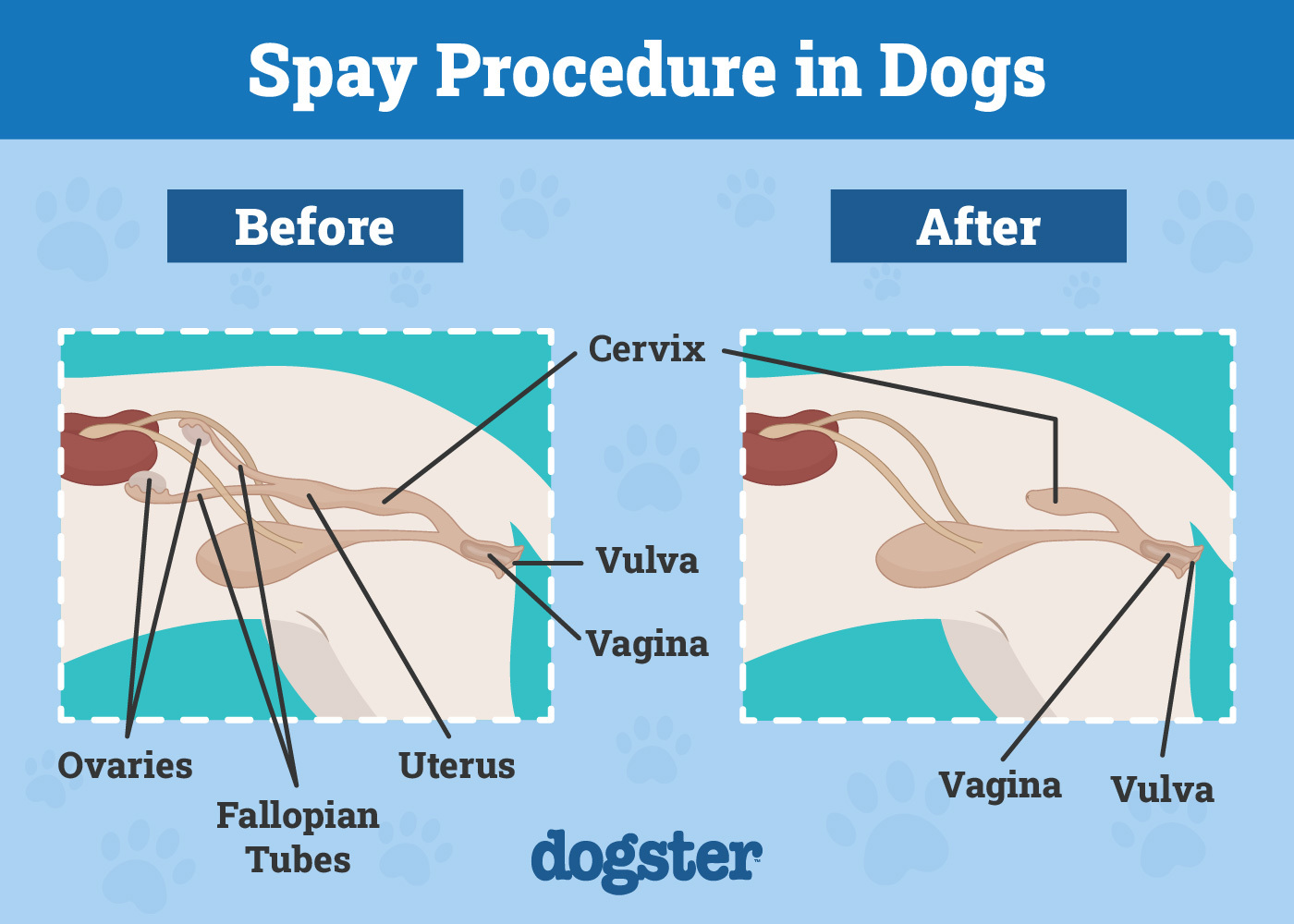
Spaying is a procedure widely used and recommended by most veterinarians for obvious reasons, such as preventing unwanted litter, reducing the risk of certain reproductive diseases, and curbing behavioral issues. The procedure is also known as an ovariohysterectomy (in which both the uterus and ovaries are removed) or an ovariectomy (in which only the ovaries are removed).
Spaying and neutering are crucial for reducing the number of unwanted litters, thereby decreasing the population of stray animals entering shelters or rescues. Moreover, these procedures offer distinct health advantages, promoting a healthier and potentially longer life for the dog while potentially mitigating behavioral problems. For instance, spaying prevents or significantly reduces the chances of severe health issues like mammary cancer and pyometra, a potentially life-threatening uterine infection.
Although there are obvious benefits to spaying, it is still prudent to consider the potential risks associated with this type of procedure.
What Research Says About Spaying Dogs
Numerous studies have been conducted to explore the link between spaying and longevity in dogs. One such study analyzed data from over 70,000 dogs and found that spayed female dogs tended to live longer than intact females; indeed, their life expectancy was 26.3% longer.1 The researchers attributed this to the decreased urge to roam and the reduced risk of reproductive-related health issues, such as mammary tumors and uterine infections, which are more prevalent in intact females.
Another study, based on the Banfield Pet Hospital database, examined the lifespan of over 2 million dogs and found similar results: Neutered males and spayed females lived longer than their intact counterparts.2 The researchers suggested that neutering may decrease the risk of certain diseases, such as testicular cancer and prostatic hyperplasia, thereby contributing to increased longevity.
However, while spaying and neutering may offer health benefits that could lead to a longer life for a dog, they are not guaranteed to extend the animal’s lifespan. Other factors, including genetics, diet, exercise, and overall healthcare, also have significant roles in determining a dog’s longevity.

The Potential Risks of Spaying
While spaying can offer health benefits, it’s essential to consider the potential drawbacks. A few studies have suggested that spayed female dogs may be at an increased risk of certain health issues, such as obesity and urinary incontinence.3 Additionally, spaying before maturity may impact skeletal development and increase the risk of certain orthopedic problems.4
According to the Humane Society of the United States, some studies seem to challenge the health advantages of widespread spaying/neutering of companion pets by suggesting that these surgeries could increase the risk of certain orthopedic conditions and cancers in altered dogs.5 Consequently, some pet owners have hesitated to alter their pets early or at all. However, upon closer examination, these studies primarily focus on male dogs of specific giant breeds (typically weighing 90–100 pounds or more), and their findings should not be generalized to other breeds or other species, such as cats.
Most studies on this topic are retrospective, meaning they analyze existing research data. Therefore, while they investigate associations between a cause and an outcome, they cannot definitively establish causality. It’s also crucial to recognize that while a study may find something statistically significant, it doesn’t always translate to a clinically significant difference. While all study designs have strengths and limitations, there’s a necessity for repeatable prospective studies (new research) conducted by various researchers across different locations and with substantial sample sizes to provide more robust data on all aspects of this topic.

FAQ About Spaying and Longevity in Dogs
At What Age Should I Spay or Neuter My Dog?
The optimal age for spaying or neutering varies greatly depending on breed, size, temperament, and overall health. Many veterinarians recommend spaying small and medium-sized female dogs before their first heat cycle, typically around 6 months of age, while spaying and neutering female and male dogs of large and giant breeds is best done at 12-15 months of age or older.
Will Spaying My Dog Prevent All Reproductive-Related Health Issues?
While spaying can significantly reduce the risk of certain reproductive diseases, such as mammary tumors and uterine infections, it does not eliminate all potential health concerns. Regular veterinary care and preventive measures are still vital for maintaining your dog’s overall health.
Can Spaying or Neutering My Dog Have Any Adverse Effects on Their Health?
While spaying and neutering are generally considered safe procedures, potential complications are associated with any surgery. Discuss the benefits and risks with your veterinarian before making a decision.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your dog — all at an affordable price!

Tips for Helping Your Dog Stay Healthy
While spaying or neutering your dog may contribute to their overall health and longevity, there are several other steps that you can take to ensure that your furry friend stays healthy and happy for years to come:
- Regular vet check-ups and vaccinations. Schedule annual wellness exams and recommended vaccinations with your veterinarian to monitor your dog’s health and catch any potential issues early.
- Balanced diet. Feed your dog a nutritionally balanced diet appropriate for their age, size, and activity level to maintain optimal health.
- Weight management. Keep your dog at a healthy weight to reduce the risk of obesity-related health problems, such as joint issues and heart disease.
- Parasite prevention. Protect your dog from parasites, such as fleas, ticks, and heartworms, through regular preventative treatments recommended by your veterinarian.
- Enrichment and Physical Activity. Provide a safe and stimulating environment for your dog, including opportunities for socialization, sufficient exercise, play, and mental enrichment.


Bottom Line
Ultimately, while spaying your dog can provide several health benefits that could contribute to a longer life, you’ll need to consider all factors before making your final decision.Be sure to discuss your concerns with your veterinarian, as they are best placed to help you decide when you should spay or neuter your beloved canine companion.
Featured Image Credit: RJ22, Shutterstock