In this article
View 2 More +Neutering/spaying dogs is common among pet owners looking to prevent health conditions, behavioral issues, and pet overpopulation. The standard is to spay or neuter the dog within the first year, but recent research suggests that castrating certain breeds can increase the risk of some cancers, joint disorders, and other health conditions, especially in large breeds.1
If you’re wondering when you should spay or neuter your Great Dane, here’s everything that you need to know.

Should I Spay or Neuter My Great Dane?
Removing the reproductive organs of male and female dogs—otherwise known as neutering or spaying, respectively—also reduces the breeding instinct and associated behaviors,2 and it may prevent serious health problems later in life, such as uterine infections, mammary gland cancer in females, testicular cancer, and an enlarged prostate in males. However, there is evidence that dogs reproductively altered at a younger age may be at increased risk for other problems later in life, such as various cancers and joint diseases.
Spaying or neutering has no effect on the dog’s intelligence, ability to learn and play, or positive behaviors, and having these procedures done prevents unexpected litters and unwanted puppies.

What the Research Says
Several studies have examined the effects of neutering (and spaying) at 8 to 16 weeks versus 6 months of age, which is a common timeframe. This research has revealed that early sterilization is not associated with an increased risk of mortality or serious health and behavioral problems when compared to neutering at 6 months.
There isn’t much data pinpointing the ideal age to neuter or spay pets, but emerging research suggests that behavioral problems, endocrine disorders, orthopedic disease, certain cancers, obesity, and urinary incontinence may be linked to sterilization status and the dog’s age. A 2013 study from the University of California-Davis conducted on Golden Retrievers showed a correlation between early sterilization and diseases like hemangiosarcoma, mast cell tumors, hip dysplasia, lymphosarcoma, and cranial cruciate ligament rupture.
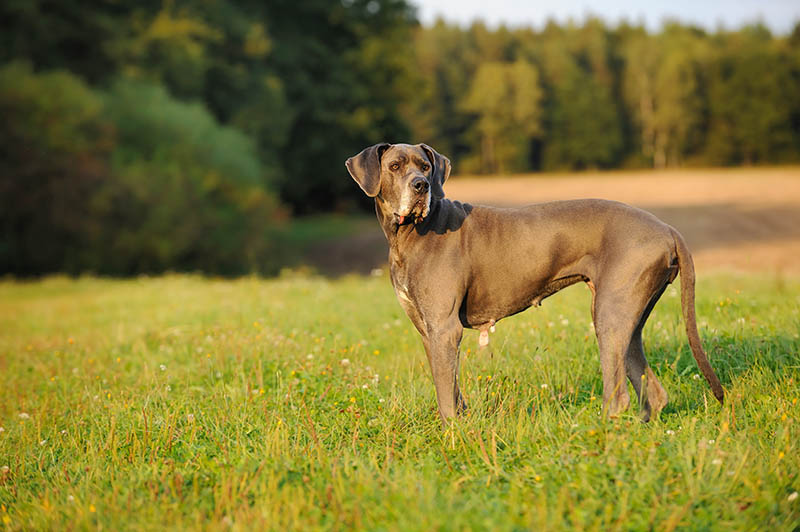
UC Davis also conducted a larger 10-year study that examined 35 dog breeds and found that sterilization risks vary significantly based on the breed. It revealed that the risk of developing problems was not affected by the age of neutering but rather by body size. Large breeds had an increased vulnerability to joint disorders compared to small breeds, though there was one surprising exception. Great Danes and Irish Wolfhounds, two giant breeds, showed no increased risk of joint disorders, no matter the age at which they were neutered.
Another notable finding was that the sex of the dog had an impact on health risks. The female dogs in the study showed no increased risk of joint disorders or cancers compared to intact dogs, which wasn’t the case for the male dogs. This is in contrast to the earlier study on Golden Retrievers, which revealed that neutering or spaying at any age significantly increases the risks of certain cancers.

When Is Spaying and Neutering Recommended for a Great Dane?
According to the AAHA Canine Life Stage Guidelines, small dogs should be neutered at 6 months or spayed prior to the first heat, which occurs between 5 and 6 months.
With large breeds like Great Danes, some vets are suggesting later neutering, ideally when the dog is done growing, which is typically between 9 and 15 months. For females, spaying should occur within a recommended window of 5 to 15 months, depending on the risks associated with the particular dog.
Based on the results of the UC Davis study showing demonstrable increase or decrease in risks associated with age of male and female Great Danes, the decision is ultimately up to the pet owner and their veterinarian. If you’re uncertain about when to spay or neuter your dog, consult a veterinarian for guidance.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your dog — all at an affordable price!


Conclusion
Historically, spaying and neutering have been performed at the earliest age possible to avoid future health problems and minimize the risks of surgery. Now, the veterinary community is evaluating the ideal age to sterilize dogs to prevent some health problems without increasing the risks of others.
Fortunately, the Great Danes is one of the few breeds that haven’t shown a significant difference in the risks associated with age. As your Great Dane’s owner, the choice is yours, along with consultation from your veterinarian to evaluate the risks and benefits for your specific dog.
See Also:
Featured Image Credit: anetapics, Shutterstock