In this article
We’ve all wondered how the world looks through our dogs’ eyes. It’s true that a canine’s vision is different from that of a human, but there’s a balance. While dogs don’t see as well as we do in some conditions and situations, their vision is superior to ours in others.
In brief, dogs see very well at night, but they don’t perceive objects the way we do and see a more limited spectrum of colors. We’ll elaborate on these differences and try to help you picture the world as your dog sees and understands it.

Can Dogs See Colors?
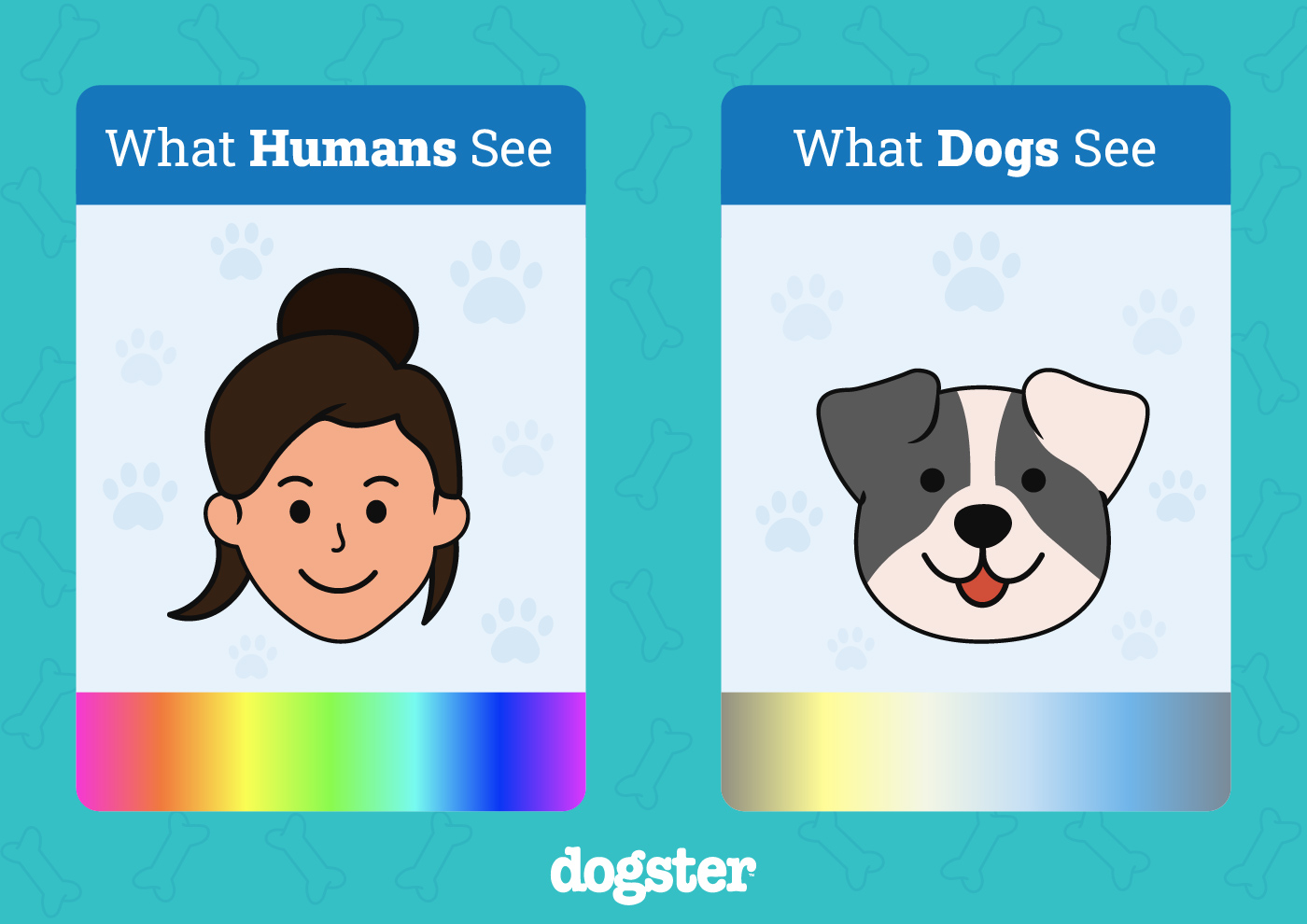
Yes, but the spectrum of colors they can perceive is less vibrant than what humans see. Canines have dichromatic vision, which means they see the world in shades of blue/purple and yellow. The full spectrum of what a dog sees ranges from a murky brown shade on one end of the spectrum to dark blue on the other.
By contrast, humans see a wide range of color variants, and they appear more vibrant to us than they would to a dog. What a human sees as red or green, a dog sees brown or gray. When we see purple, dogs only see blue, and so on.
This happens because humans have three types of cones—photoreceptor, or light-sensitive, cells that enable us to see colors—which are red, green, and blue. Conversely, dogs have two varieties that enable them to see only blue and yellow.
Can Dogs See in the Dark?
Night vision is an area in which canine vision triumphs over human vision. In the previous section, we touched on how the retina contains cones, which are one type of photoreceptor. There is another kind of retinal photoreceptor cells, and these are called rods.
While cones are responsible for color vision, rods enable you to see in low-light conditions. Canines have more rod cells in their retinas than humans (who have more cones), meaning they can make the most of any amount of light available.
In addition, dogs have large pupils, which enable more light to enter the eyes, and a tapetum lucidum, a reflective layer in the back of each eye, just behind the retina. This layer behaves as a mirror of sorts that reflects light back and increases the chance that the photoreceptors will pick it up. Unlike canines, humans don’t have a tapetum lucidum.
Dogs have adapted to see well in the dark because their wild ancestors would hunt mostly when lighting conditions were low. They are crepuscular animals rather than nocturnal, meaning their most active hunting periods are at dusk and dawn.

Dogs & Motion Perception
As explained in a 1963 study, canines are better at detecting moving targets than they are at detecting stationary ones. Dogs can see a moving object from a distance of 900 meters, whereas stationary ones are detected at 585 meters.1
In addition, when dogs watch TV, if the refresh rate is under 75 hertz, they will see flickers. In contrast, with TVs with a screen-refresh rate above 55 hertz, humans don’t see flickering.
However, a study published in 2017 found that dogs don’t detect coherent motion better than humans do. During the study, dogs were trained to touch a screen displaying coherent motion. The other screen showed dots moving in a non-coherent motion. The results showed that dogs have a threshold of 42% for detecting coherent movement, while humans have a threshold of 5%.2
Dogs & Depth Perception
Though dogs have a broad visual field, being able to see 240 degrees without turning their heads, their depth perception (how well they perceive the size of 3D objects and their distance away) is weaker than that of a human.
Canines have less binocular overlap due to the position of their eyes. However, the ability to perceive depth can be determined by the breed, as different breeds have different eye positions and skull shapes. For example, a Bulldog’s depth perception is stronger than that of a Whippet.

Dogs & Visual Acuity
The average human’s visual acuity (sharpness) is 20/20, meaning they can clearly see objects at a distance of 20 feet, which is considered normal vision for humans. Conversely, canines have 20/75 vision, so they must be at a distance of 20 feet to perceive an object as a human would from a distance of 75 feet. In short, a dog’s vision isn’t as sharp as a human’s.
Dogs & Visual Perspective
Dogs are limited in their ability to see upward because their height compared to that of a human means their vision is naturally angled toward the ground. Unfortunately for dogs with longer skulls, their snouts can get in the way of their downward vision too. These dogs need to lower their heads to get a good look at the ground.
Does a Dog’s Vision Get Worse as They Age?
It can. Older dogs are more likely to experience age-related eye problems. These can happen due to changes in the lens, such as cataracts, retinal diseases, and other eye conditions like glaucoma and corneal degeneration.
Signs your senior dog may be experiencing poorer vision include (but are not limited to) the following. Please see a vet if you notice any of these signs.
- Bumping into things
- Lethargy
- Lack of eye contact
- Struggling to find things they once could
- Confusion
- Startling easily
- Changes
- Clinginess
- Eye cloudiness
- Being hesitant to jump up on or down from furniture
- Not wanting to go up and down the stair
- Physical clues like eye redness or swelling
If you want more information or are concerned about the health of your pet, you should contact your vet.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your pet — all at an affordable price!

Final Thoughts
In summary, dogs have strong night vision and a broader field of vision than humans, and they are better at spotting moving targets than still ones. However, their vision is not as sharp when compared to that of a human. Canines also perceive a limited spectrum of colors compared to what humans see.
If you’re concerned about your dog’s vision in any way, please consult with your vet to make a plan for treatment and/or management.
See also:
Featured Image Credit: Javier Brosch, Shutterstock