In this article
View 3 More +Did you know that some studies show that our pets have larger brains than their ancient relatives?1 It’s worth noting that we challenged dogs by selectively breeding them for different jobs, which could definitely be a contributing factor. But then, you come to the petite Chihuahua and wonder just how big their brains can be when they come in such a petite package. Research has shown the ratio between a dog’s body weight and brain weight is about 125:1. For humans, it’s about 40:1, although this is a helpful but not hugely accurate estimate.
However, a Chihuahua’s brain weighs about 55.10 grams or 1.944 ounces in a dog weighing 7.6 pounds or 3.35kg. That comes out to around 1.6% of their body weight. The typical human’s brain is about 2% of an individual’s body weight. For example, that’s 3 pounds for a 150 pound person. That gives us the basics for determining the size of this pup’s brainpower.

About the Encephalization Quotient
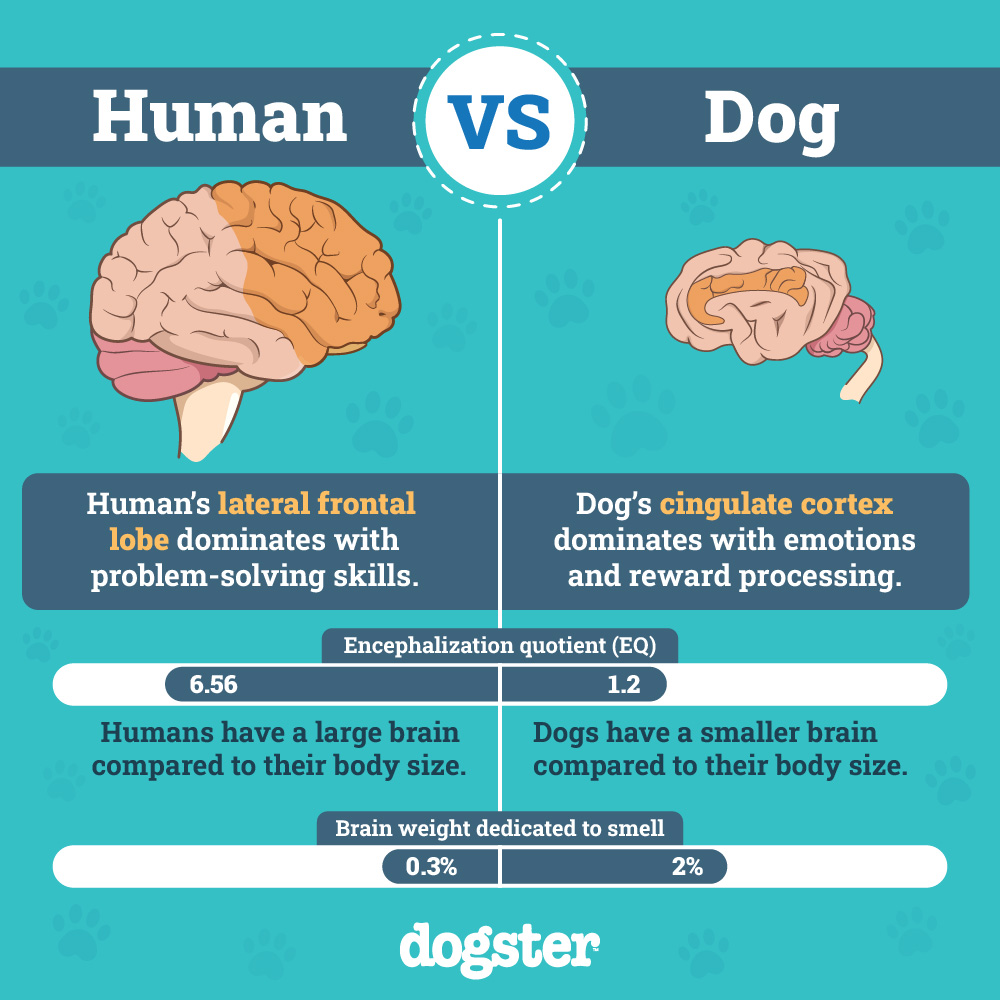
That brings us to the concept of the encephalization quotient (EQ), which describes the measure of relative brain size and is used to convey how small or large an animal’s brain is compared to animals of a similar body size. It essentially gives us a way to compare intelligence across species lines. An EQ of 1 equates to the brain mass expected for the group. The EQ of humans is approx. 7, meaning that our brain mass is 7 times greater than the average mammal. Nevertheless, a canine brain has the same hardware as ours but an EQ of 1.2 which is only slightly better than the average mammal.
Dog Intelligence
We must also consider the role that Chihuahuas serve for humans. Breeds selectively bred for specific traits and functions are relatively new, occurring around 180 years ago. These pups’ executive functions revolved around being companion animals. That makes them well-attuned to humans and their activities and personalities, and these varying roles nurture various traits.
The German Shepherd Dog (GSD) is the second or third most intelligent dog breed (depending on which source you read). Research that quantified the Chihuahua’s brain size puts the GSD brain weight at 3.03% of its average body weight.2 That puts this breed in the realm of humans in terms of percentage body weight made up by brain weight. The Chihuahua has a lower percentage, but nevertheless, it is capable of doing a range of tasks. However, the difference lies in what we expect from these dogs.
Think of the German Shepherd Dog’s original role as a herder. This job demanded intelligence and problem-solving skills. Meanwhile, being a companion animal like a Chihuahua didn’t involve the same demands.

Dog Brains vs Human Brains
Outlining the variations between canine and human brains is essential to understanding the size differences fully. Size is only one metric. The real issues lie with what the species can do with their hardware. There are many DNA similarities between humans and dogs. In fact, we share 84% of our DNA with dogs.
Scientists have identified voice areas in the canine brain that show a similar pattern to the voice areas of a human brain.3 Canines recognize our emotions, perhaps partly because they experience feelings on a par with a young child. These skills are what a Chihuahua needs to know as an animal companion, and the size of the breed’s brain is adequate to be able to meet these needs.

Human Influences on the Canine Brain
Interestingly, dogs show a wide range of variations in their skull size and shape, therefore impacting their brain anatomy. For example, breeds like Chihuahuas have more spherical-shaped heads and brains compared to, say, a Golden Retriever, which has long muzzles and larger sinuses or open areas between the brain and skull.
Differences between the breeds are also evident within specific networks in the brain.
- Olfaction and vision
- Fear, stress, and anxiety
- Social action and interaction
- Movement, eye movement, and spatial navigation
- Olfaction and taste
- Drive and reward
Additional research is needed. However, these initial findings show the profound influence selective breeding has had on dogs. The Chihuahua brain may not only differ in size and proportion to body weight, but it may also have an anatomy that reflects their role as companion animals and their traits that make them good at this job. So, we’d expect it to look very different from that of a Border Collie or German Shepherd Dog.
Science has shown that all mammals possess neural stem cells capable of developing new nerve cells. More research is necessary to identify the precise mechanism. However, it lends support to our theory that the Chihuahua brain is unique to the breed, as seen in the relationship between brain size, skull size and shape and the volumes of the six identified networks.
We can examine the findings of the network study for additional evidence. One fascinating finding was the correlations between the networks and the primary functions of the breeds, modeling the American Kennel Club’s group organization. Animals kept explicitly for companionship ranked highest in drive and reward.
Other research has revealed that larger dogs have corresponding bigger brains. They excel at executive functions over non-working breeds like the Chihuahua. They also performed better with skills relying on short-term memory and self-control. Remember that people didn’t start selective breeding in earnest until about 160 years ago. That implies our genetic impact on dogs happened quickly.
However, many canines don’t do the jobs for which they were bred. While Collies might compete in the show ring, not that many are herding sheep. Therefore, we can expect the brain anatomy of these animals to evolve as their jobs change. That may be true for many, but it may not be true for Chihuahuas. The breed has a long history as an animal companion that isn’t likely to change any time soon.


Final Thoughts
The Chihuahua may have a relatively small brain, but they hold a big place in our hearts as loyal canine companions. This role is evident in the dog’s brain anatomy. They are born to please us with unconditional love. However, science has much to learn about the canine brain. Maybe the Chihuahua and other breeds have more secrets to share with us.
Featured Image Credit: Erwin Bosman, Shutterstock