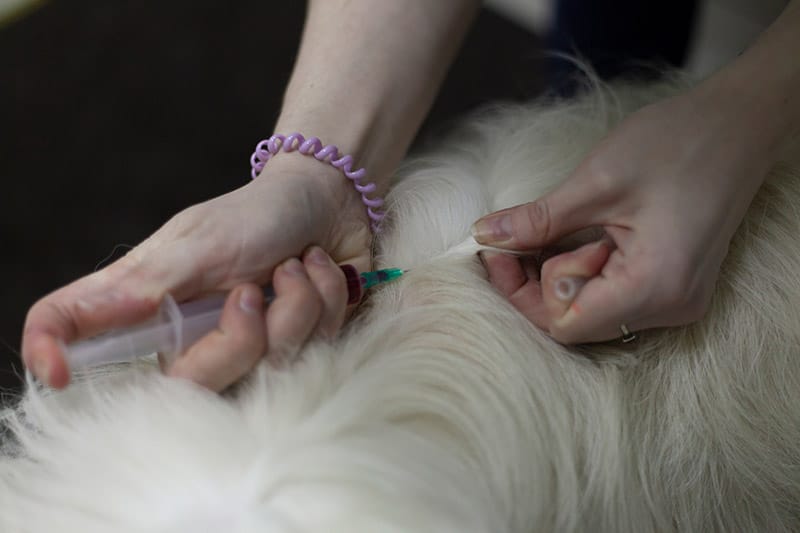
The stress level of taking your dog to the vet for their annual shots can depend on the situation and the individual dog. Some dogs are far more stressed about vet visits than others, and some dogs think going to the vet is just as fun as a trip to the park.
Regardless of where your dog falls on the spectrum, it can be stressful for you as a pet owner to bring your dog home after their shots, only to discover that they seem to have swollen lymph nodes. Is their vaccine the cause, though? And should you be concerned about this? In short, yes, vaccines may make your dog’s lymph nodes swell. Although this reaction is quite common, let’s explore what to do, especially when your dog has other distressing signs.

Can Vaccines Make Lymph Nodes Swell?
Lymph nodes are small organs that contain immune cells. So, when your dog’s body gets invaded by bacteria or viruses, the lymph nodes may enlarge as they work to fight off the invader. Lymph nodes are an essential component of your dog’s immune system. Swelling of the lymph nodes after getting a vaccination is often a response brought on by the immune system reacting to the presence of the vaccine components, similar to the way they would react to a microbe.
Swollen lymph nodes can be a side effect of having vaccines. Side effects are not the same thing as allergies, though, so swollen lymph nodes after vaccines don’t necessarily mean that your dog is allergic to the shots they received. Side effects can be mild to severe when it comes to any vaccine or medication.
If you notice swollen lymph nodes after a vaccination, it’s probably best to give your vet a call and let them know, especially if they’re happening alongside other negative signs, such as vomiting, coughing, fever, lethargy, or poor appetite. If you notice swollen lymph nodes at any other time, be sure to contact your veterinarian.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your dog — all at an affordable price!
What if My Dog Has Swollen Areas Elsewhere?
Your dog has five sets of lymph nodes in their body, including the neck (submandibular), chest (prescapular), armpit (axillary), groin (inguinal), and knees (popliteal). Swelling can occur in any of these lymph nodes.
If your dog has swelling that is right near the area where they received their vaccine, then there’s a chance that they’re experiencing localized swelling from the shot.
Like lymph node swelling, swelling at the site of an injection is likely an inflammatory immune response to the introduction of a foreign substance. This swelling typically goes down on its own within 24–48 hours. If the swelling at the vaccine site does not begin to go down within a day or so, or if the swelling increases, the area becomes hot, or your dog is experiencing extreme tenderness, then you should have your vet check on your dog. There is a risk of infection with any type of injection, and it’s also possible for your dog to experience a more severe reaction.
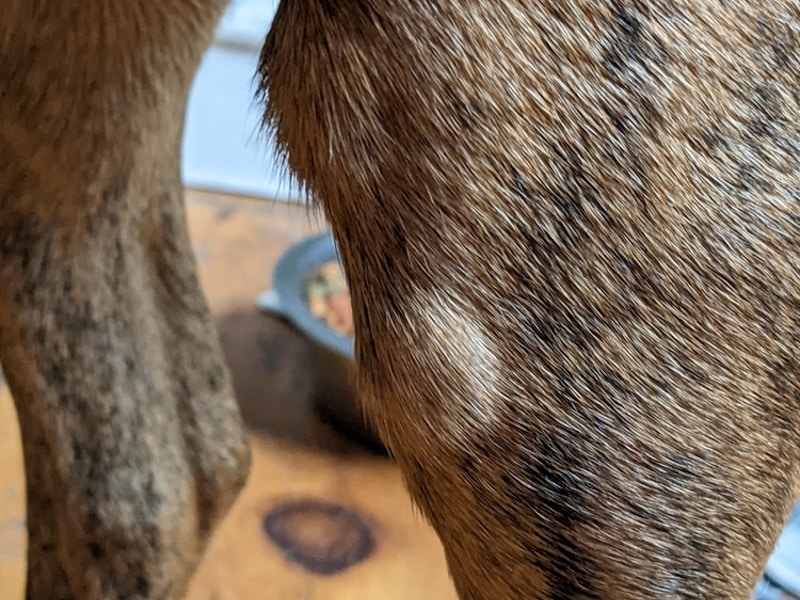

What Should I Do if the Swelling Is Increasing?
If the swelling around your dog’s lymph nodes seems to be increasing, then they need to be seen by a veterinarian. If your dog is experiencing an increase in swelling shortly after the vaccine, then they may be having an allergic reaction.
Swelling of the face, tongue, or throat should be considered a medical emergency because it can rapidly lead to anaphylaxis and an inability to breathe. If you’re unsure if the swelling your dog is experiencing is something you should be concerned about, then don’t hesitate to call your vet or take your dog back to the clinic for a check-over.


In Conclusion
Swollen lymph nodes can be a side effect of vaccines that indicates that your dog is experiencing an immune system response. There isn’t necessarily any reason to be concerned if this occurs, but significant swelling, swelling that lasts longer than 24 hours, or swelling that spreads to the throat, mouth, or face should be addressed by a veterinarian. When in doubt, it’s always best to give the vet a call, just to be safe.
Featured Image Credit: Oleg Kopyov, Shutterstock