In this article
View 2 More +Non-steroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) are used to treat various issues in canines, from short-lived treatment like spay surgery pain to long-term use for osteoarthritis. For most dogs, NSAIDs provide them with pain-free mobility, but using them in the long run can come at a cost. That’s why NSAID panels are so vital.
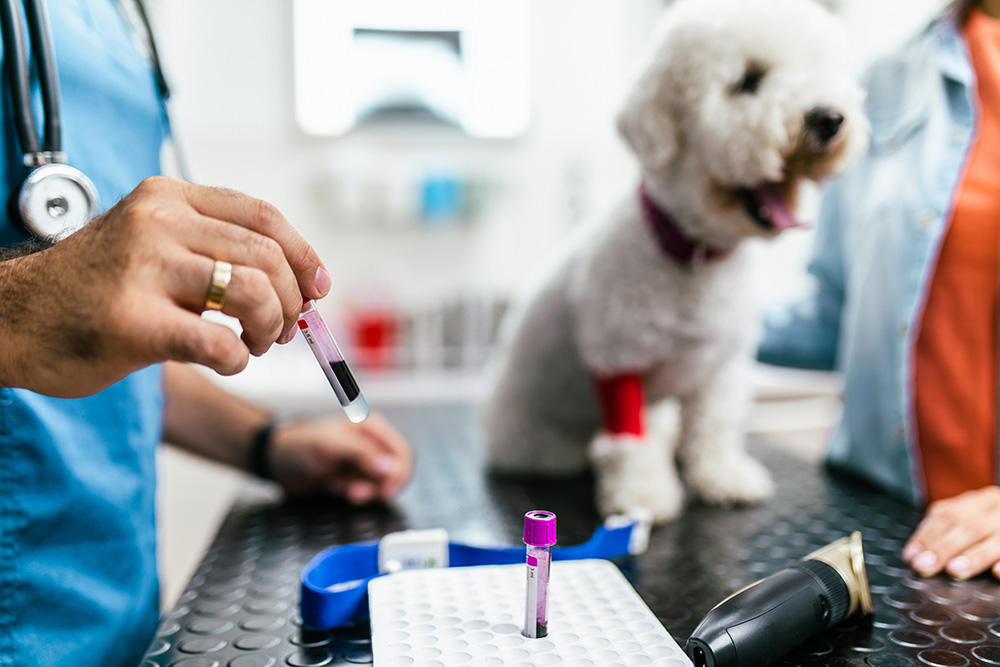
These blood tests help check the effects that the prescribed NSAID may be having on the dog’s major organs. As a rule, they should be performed before starting treatment and then periodically throughout the process. The frequency will depend on the dog and the situation.

What Is an NSAID Panel for Dogs?
NSAIDs can work wonders at reducing inflammation and pain from all sorts of ailments. Unfortunately, they may also be negatively affecting certain parts of the body. The digestive system, kidneys, liver, and blood cells are the most common victims.
Keep in mind that side effects are more likely to occur at high doses and when taken with other medications, but they can still happen to an otherwise healthy dog taking only normal levels of NSAIDs.
To monitor these targeted organs, periodically doing an NSAID blood panel can be beneficial. It will help the veterinarian see if the rest of the dog’s body is operating optimally or if there’s an upset that needs to be addressed, hopefully before something serious can happen. An NSAID blood panel should check at least the liver values of ALT, ALP, and AST and the kidney values of BUN and creatine. That said, it doesn’t have to be limited to these and may include a red blood cell count, among other tests.
Alongside an NSAID blood panel, you and your vet should monitor how well the NSAID is controlling your dog’s pain and health in general, including appetite, attitude, and pooping and peeing.
How Often Should an NSAID Blood Panel Be Done?
Monitoring your dog’s response to NSAIDs is a crucial piece of the management puzzle, but the frequency for monitoring isn’t one-size-fits-all. How often you have the blood tests performed will be up to you and your vet. As a general rule, though, every dog should have blood work done before starting NSAIDs, to make sure their body is ready for this medication and to get a baseline of their values.
Since most adverse drug reactions occur within 14–30 days of starting the medication, an NSAID blood panel should be done 2–4 weeks after starting. Of course, if the owner notices any changes in their dog’s appetite or signs like vomiting or diarrhea, repeat blood work can be done sooner.
After that starting phase, the frequency of NSAID blood panels will likely depend on your dog’s age and any other health concerns. For canines over 10 years old, blood tests may be recommended every 3 months. Pups younger than 10 may get by with every 6–12 months. Again, if a dog experiences any adverse effects, speak to your vet rather than wait for your pet’s next scheduled blood panel.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your dog — all at an affordable price!
Are Blood Panels Necessary for Dogs on NSAIDs?
Fortunately, severe adverse reactions to NSAIDs are incredibly rare, but it can be catastrophic when they do happen. Therefore, keep a close eye on your dog’s bodily functions at home and the vet’s. NSAID blood panels are the best way to do this, especially if your dog will be taking the medication for the long term. Constant monitoring at home is just as important, though, and should be frequently discussed with your vet.


Conclusion
NSAIDs are frequently used and effective medications for dealing with a dog’s inflammation, but they are far from perfect. They can have side effects that affect the liver, kidneys, and digestive system, especially when taken at high doses or for the long term.
Any canine taking an NSAID for longer than a couple of weeks should receive regular NSAID blood panels before beginning the medication and after 2–4 weeks with it onboard to check organ function. After that, it depends on your pup’s age and your vet’s discretion, but they’re typically done every 3 months for dogs over 10 years and every 6–12 months for pups younger than that.
Featured Image Credit: hedgehog94, Shutterstock