We’ve all heard of cats coughing up hairballs, but is this something you should be concerned about with your dog also? Although it’s not common, dogs can get hairballs. Hairballs, known medically as trichobezoars, can cause serious problems for dogs, so it’s important to recognize the signs and get your dog’s hairballs taken care of if necessary.

Why Do Dogs Get Hairballs?
In order to get a hairball, your dog must consume hair. Some dogs may unintentionally do this when grooming themselves, while others may simply consume hair out of curiosity or due to a condition known as pica. Trichobezoars can consist of any type of hair, including human, canine, and feline.
Hair is rich in keratin, which is a structural protein that is not able to be digested. Typically, consumed hair would simply pass through the body and be excreted in the waste in its whole form. However, if your dog consumes a large amount of hair, especially in a short period of time, then the hair may not be able to pass out of the stomach. This will cause the hair to build up as your dog continues to consume more of it. In some cases, the hair may pass into the intestines and create an obstruction there.

What Happens When a Dog Gets a Hairball?
Like cats, many dogs can vomit up hairballs. Over time, the buildup of hair will create bloating and discomfort in the stomach, leading to nausea and vomiting in an attempt to pass the hairball. In cases where the hairball isn’t vomited up, it may become lodged in the stomach or intestines, creating an intestinal obstruction.
If your dog experiences an intestinal obstruction from a hairball, they will need surgery to remove it. For smaller hairballs that are still in the stomach there can be an option of removal using an endoscope, which reduces the invasiveness.
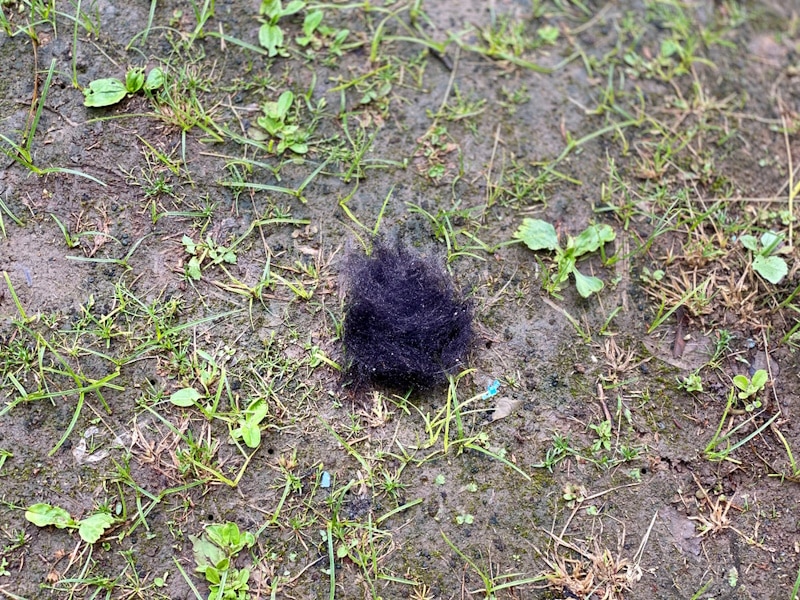

What Are the Signs of a Hairball?
Oftentimes, the first sign that your dog has a hairball will be that you see them vomit up a hairball. Hairballs are often cylindrical in shape, almost like a large, semi-solid pellet.
If your dog isn’t able to vomit up the hairball, then there are multiple signs you may notice. Loss of appetite, abdominal pain, nausea and repeated vomiting, constipation, and hacking or attempting to vomit can all indicate that your dog has an intestinal obstruction or is attempting to pass a hairball. Many other medical conditions result in similar signs. If your dog is exhibiting any of these signs, you should contact your vet for evaluation.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your pet — all at an affordable price!
Can Any Dog Get a Hairball?
Yes, any dog can have a hairball. Dogs with skin conditions seem to be at higher risk of hairballs, though, since they frequently lick and chew at their skin and coat. This can lead to unintentionally swallowing a large amount of hair. Long-haired dogs that frequently lick and groom themselves may also be at increased risk, as well as dogs that are known to simply eat hair when they find it.

Conclusion
Hairballs can become a life-threatening problem for your dog, so treatment and prevention are both important. The good news is that hairballs aren’t particularly common in dogs, but if your dog is at high risk for a hairball, you should keep an eye out for the onset of any potential hairball signs. If your dog vomits up a hairball, you may need to talk to your vet to come up with a prevention plan for the future.
Featured Image Credit: TongRoRo, Shutterstock