Disclaimer: This article has been fact-checked by a qualified veterinarian using information available at the time of review. Veterinary medicine is continually evolving and changing. Dog owners are urged to discuss their dog’s care with their veterinarian and this article should not be taken as a substitute for medical advice for your pet.
Have you noticed your furry companion heading to the backyard or their pee pad more often than usual? While excessive urination in dogs can simply be a sign that they are staying hydrated and drinking plenty of water, it can also be a sign of underlying health issues. As a pet owner, you should know the various reasons behind this change in behavior, so you can determine if it’s simple or serious. Keep reading for a list of the most common causes and when it’s time to call the vet.
The 9 Reasons That Your Dog Might Be Peeing a Lot
1. Increased Water Intake
One of the most likely reasons your dog is peeing frequently is that they are drinking more water than usual. Dogs may drink more water for various reasons, such as hot weather, increased physical activity, dietary changes, or even a reaction to salty treats. More water going in naturally leads to more frequent urination. However, they could be drinking more due to health concerns so read on to find out more.
2. Urinary Tract Infection
Urinary tract infections are bacterial infections that affect the urinary tract. Signs include frequent, often urgent urination in small amounts, discomfort during urination, bloody or cloudy urine, and excessive licking of the genital area. Urinary tract infections are more common in female dogs and might require antibiotics prescribed by a veterinarian.
3. Diabetes
In dogs, diabetes can cause increased thirst and urination because the dog’s body isn’t using glucose properly, and the kidneys have to work harder to eliminate the excess glucose in the blood. This process requires more water, hence more drinking and urination. Other signs include weight loss, increased appetite, and cataracts.
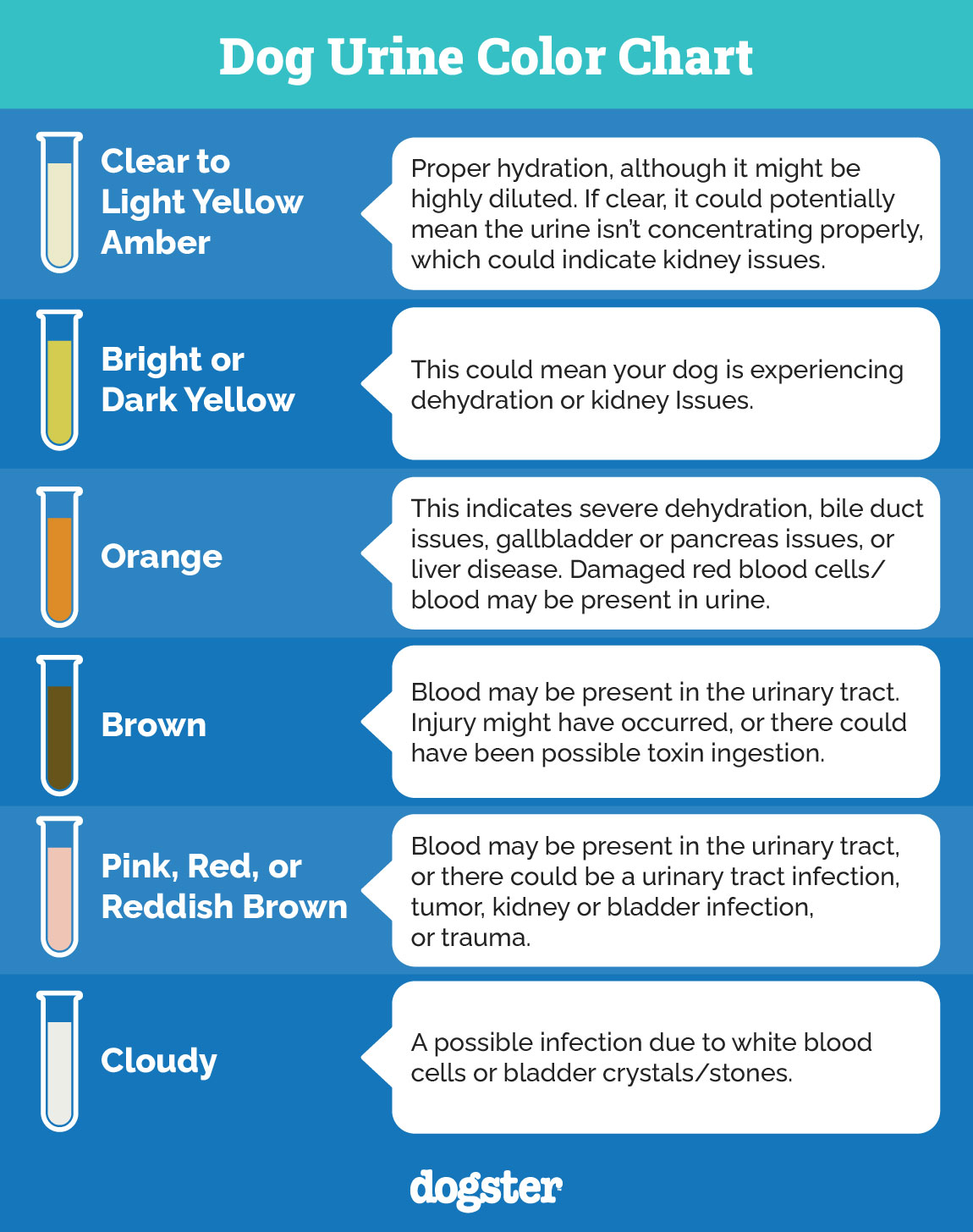
4. Kidney Disease
Chronic or acute kidney disease leads to the kidneys becoming less efficient at filtering waste, causing the dog to drink more water to help flush out toxins, which results in increased urination. When your dog has kidney disease, you may also notice signs like loss of appetite, weight loss, vomiting, lethargy, and a dull coat. Kidney disease is more common in older dogs.
5. Bladder Stones
Bladder stones are mineral formations in the bladder that can cause irritation and lead to frequent urination. They can cause discomfort, difficulty urinating, and blood in the urine. The dog may attempt to urinate frequently but can only produce small amounts of urine. Treatment depends on the type of stone and may include dietary changes, medication, or surgery.
A vet will be able to advise you on the best course of action to ensure the well-being of your pet.
If you need to speak with a vet but can't get to one, head over to PangoVet. It's our online service where you can talk to a vet online and get the advice you need for your pet — all at an affordable price!
6. Hormonal Imbalance
Conditions like Cushing’s disease, Addison’s disease and hypothyroidism can affect urination. They are often accompanied by signs like increased thirst, changes in appetite, coat condition, energy levels, and weight.

7. Behavioral Issues
Increased urination can sometimes be a sign of stress or anxiety, especially if the urination occurs in specific situations, such as when the dog is left alone, or if there are other signs of stress, such as destructive behavior or excessive barking.
8. Medications
Certain medications, particularly diuretics, which a dog might receive for heart failure, and other issues, can increase urination because they help remove fluid from the body. Always check if increased urination started after beginning a new medication regimen, and consult with your vet if you suspect that it might be the cause.
9. Age-Related Issues
In older dogs, incontinence or weakened bladder control can lead to more frequent urination, not due to an increase in urine production but a decrease in the ability to hold it. Age-related diseases like cognitive dysfunction can also affect a dog’s ability to control urination, which can lead to accidents around the house.


Frequently Asked Questions
Could a Change in My Dog’s Diet Cause Increased Urination?
If your dog is eating regular dog food and always has access to water, a change in diet is unlikely to make a big difference in the amount they are urinating.
What Should I Do If I Notice Changes in My Dog’s Urination Habits?
You’ll need to consult a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause and ensure that your pet receives appropriate treatment. Keep a record of any other changes in behavior or health to assist in the diagnosis.
Can Weather or Climate Affect My Dog’s Urination Frequency?
Yes, in hot weather, dogs may drink more to stay hydrated, leading to increased urination. In cold weather, some dogs may not want to go outside as often, which can also affect their urination routine.
Are Certain Dog Breeds More Prone to Urinary Issues That Cause Increased Urination?
Some breeds may be predisposed to certain urinary health issues. For example, Dalmatians have a higher risk of developing bladder stones and poodles are prone to Addison’s disease.
How Can I Monitor My Dog’s Water Intake and Urination at Home?
Each day measure the amount you put in your dog’s water dish and measure how much is left before you top it up again; the difference is the amount your dog has drank (unless sharing with other pets). If you notice your dog is visiting the water bowl more frequently and spending longer drinking, this is a strong sign of increased thirst. Also, observe the frequency and amount of your dog’s urination as best as possible, and watch for changes in color or odor.
What Can I Do to Help Manage My Dog’s Increased Urination?
To help manage your dog’s frequent urination, seek veterinary help to treat the underlying cause. Give them regular bathroom breaks, maintain a consistent routine, provide a balanced diet, ensure adequate hydration, and create a stress-free environment.

Summary
If your dog is peeing a lot, it is most likely because they have increased thirst or a problem in the bladder. Dogs drink more when they are thirsty due to warm weather or salty treats, but excessive thirst is an important medical symptom that should not be ignored. If frequent urination remains persistent or there are other signs present, such as a bad odor, cloudy or bloody urine, or straining to urinate, it could be a sign of a health issue, and we recommend scheduling a visit with the vet immediately.
See Also:
- Why Is My Female Dog Peeing on the Bed All of a Sudden? 8 Vet-Reviewed Reasons
- Why Is My Dog’s Pee Green? 5 Vet Reviewed Reasons & What to Do
Featured Image Credit: Heinz Teh / Shutterstock.